At the solar and wind power plants (SPP / WPP) an accumulator batteries (ACB) accumulate electricity during the day and store its surplus. Using ACB it is possible to ensure own house with an autonomous power supply, for example:
- with aim to use the electric power which has been accumulated during the daylight hours at night or at the periods of windless weather;
- in the cases of frequent disconnections from the power grid or during the hours with high electricity consumption;
- at moments of the maximum load, if SPP or WPP cannot fully ensure electricity during such period.

Any electrical accumulator could be shown as reusable source of a constant current (charge / discharge). Different types of accumulators differ with the number of charge/discharge cycles, operation temperature range, high-speed charging capabilities etc.
THE ACB SHOULD MEET CERTAIN REQUIREMENTS FOR SPP/WPP:
- low self-discharge (to save capacity of the battery during storage or when it is not in use );
- possibility to operate in the deep discharge mode (to extend the operational life of the ACB);
- operation with the small currents;
- operation at low temperatures (to be used during the whole year) or at the periods of windless weather;
- minimum maintenance requirements.
TYPES OF THE ELECTRIC ACCUMULATORS:
- lead acid battery type;
- alkaline battery type.
Lead acid accumulator is the most commonly used type of the battery for SPP/WPP. Such batteries could be distinguished by the manufacturing technology:
- Absorptive Glas Mat (AGM) with separator made of the absorbent glass microfiber.
- Gelled Elektrolite (GEL) where the electrolyte gel is used.
In average the operational life of such accumulators is around 5 to 10 years.
The estimated cost of the ACB makes from $ 100 to 700 depending on its capacity.
Attention should be paid to the following measures when choosing the ACB for autonomous electricity supply: the depth of discharge and battery capacity.
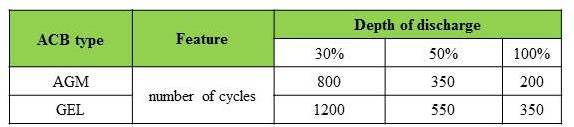
AGM accumulators can withstand up to 200 cycles of discharge with 100 % depth, 350 cycles with 50% depth and up to 800 cycles with 30% depth. Under the optimal temperature (15-25°C) and under condition of keeping the accumulator charged its operational life would correspond to the one stated by the producer or even longer.
GEL accumulators can withstand up to 350 cycles of discharge with 100 % depth, 550 cycles with 50% depth and up to 1200 cycles with 30% depth. An important feature of the GEL batteries is their resistance to deep discharges.
Such accumulators could remain fully discharged for several days causing no harm to its capacity.
COMPARISON OF THE ACB FEATURES
Probably the capacity is one of the most important parameters to choose the accumulator. Ampere-hour (Ah) is the unit used for capacity measurements. The higher is the capacity the longer the accumulator would remain in operational.
In order to determine the required capacity it is necessary to know the voltage of accumulator, the power of the load and the required number of ACB autonomous operation hours.
Let’s consider the example of selection of the ACB for autonomous operation during 1 hour with total load capacity of 1000 W.
To do this, we should choose the accumulator with voltage of 12 V and define current consumption of the devices:
I=(P/U)=1000 (Вт)/12(В) = 83, 33 (А)
Then we shall multiply defined current to the desired time, i.e. 83.33 A × 1 hour = 83.33 A∙h . Also we should consider losses during voltage conversion from 12 V to 220 V in the uninterrupted block (about 10 %), i.e. 83,33 × 1,1 = 91,663 A∙h .
So you need the accumulator with capacity of 100 A∙h. On average such accumulator is worth $ 210.
COMPARATIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ACB BY ITS VOLTAGE AND CAPACITY
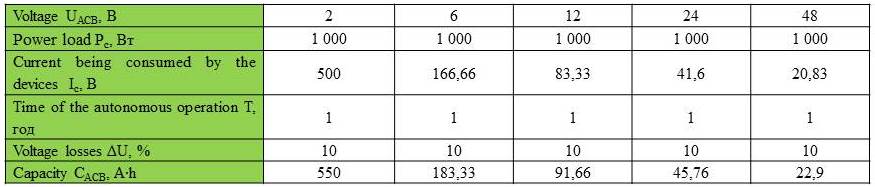
Thus, the lower is the ACB voltage the more capacity it has, and therefore the longer is the operational lifetime because less charge/discharge cycles would be applied to the battery.







